If you experience ongoing pain in the area near your ear, your jaw or the muscles on the side of your face, possibly accompanied by a clicking or popping sound or restricted jaw movement, you may be suffering from TMD — an abbreviation for Temporomandibular disorders. Sometimes people incorrectly use the term TMJ to refer to these problems, when in fact TMJ is the abbreviation for the temporomandibular joint — or jaw joint — itself. So while you definitely have a TMJ (two of them in fact), you may or may not have TMD.
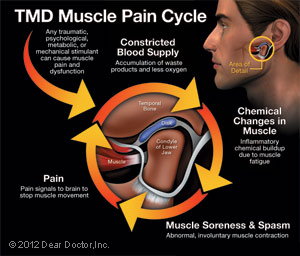
TMD, then, describes a group of conditions characterized by pain and dysfunction of the TMJ and/or the muscles surrounding it. It's not always so easy to figure out exactly what's causing these symptoms, but the good news is that most TMD cases resolve themselves with the help of conservative remedies that you can try at home. In fact, it's important to exhaust all such reversible remedies before moving on to anything irreversible, such as bridgework or surgery.
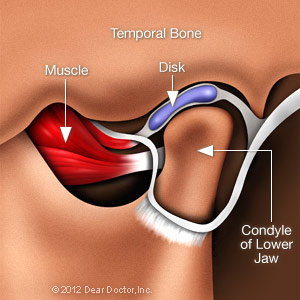
The two TMJs that connect your lower jaw, the mandible, to the temporal bone of the skull on either side, are actually very complex joints that allow movement in three dimensions. The lower jaw and temporal bone fit together as a ball and socket, with a cushioning disk in between. Large pairs of muscles in the cheeks and temples move the lower jaw. Any of these parts — the disk, the muscles or the joint itself — can become the source of a TMD problem. If you are in pain, or are having difficulty opening or closing your jaw, a thorough examination can help pinpoint the problem area; then an appropriate remedy can be recommended.